Units and Mesaurements
- Square feet (Sq. ft) (chadarapu adugulu) (చదరపు అడుగు) = 144 Sq. inches (చదరపు అంగుళం)
- Cent (సెంటు) = 435.6 Sq. ft
- Guntha (గుంట) = 1089 Sq. ft
- Square yard (gajam) (గజము) = 9 Sq. ft
- Acer (ఎకరం) = 43560 Sq. ft
- Hectare (హెక్టారు) = 107639 Sq. ft
Land Unit Converter
Approvals


1. Land Title
The first and foremost requirement before embarking on any construction project is to ensure that the land has a clear title. A clear land title means that the ownership of the land is undisputed, and there are no legal encumbrances or disputes associated with it. This involves thorough due diligence and verification of land records
Issued by : Sub-Registrar's office



2. Land Clearance
In India, land is often designated for specific purposes such as agricultural, commercial, or residential use. If the land you intend to build on is classified as agricultural or any other non-residential use, you must obtain land use conversion approval from the local authorities. This process involves submitting an application to the respective revenue department or urban development authority, demonstrating the intended use of the land.
Issued by : Revenue Department



3. Zonal Clearance
Before designing the building plan, it is essential to understand and comply with the local zoning laws and land use regulations. Zoning laws dictate the types of structures that can be built in specific areas, building heights, setbacks, and other parameters. Adhering to these regulations is crucial to avoid any legal complications during the construction process.
Issued by : Zonal Department



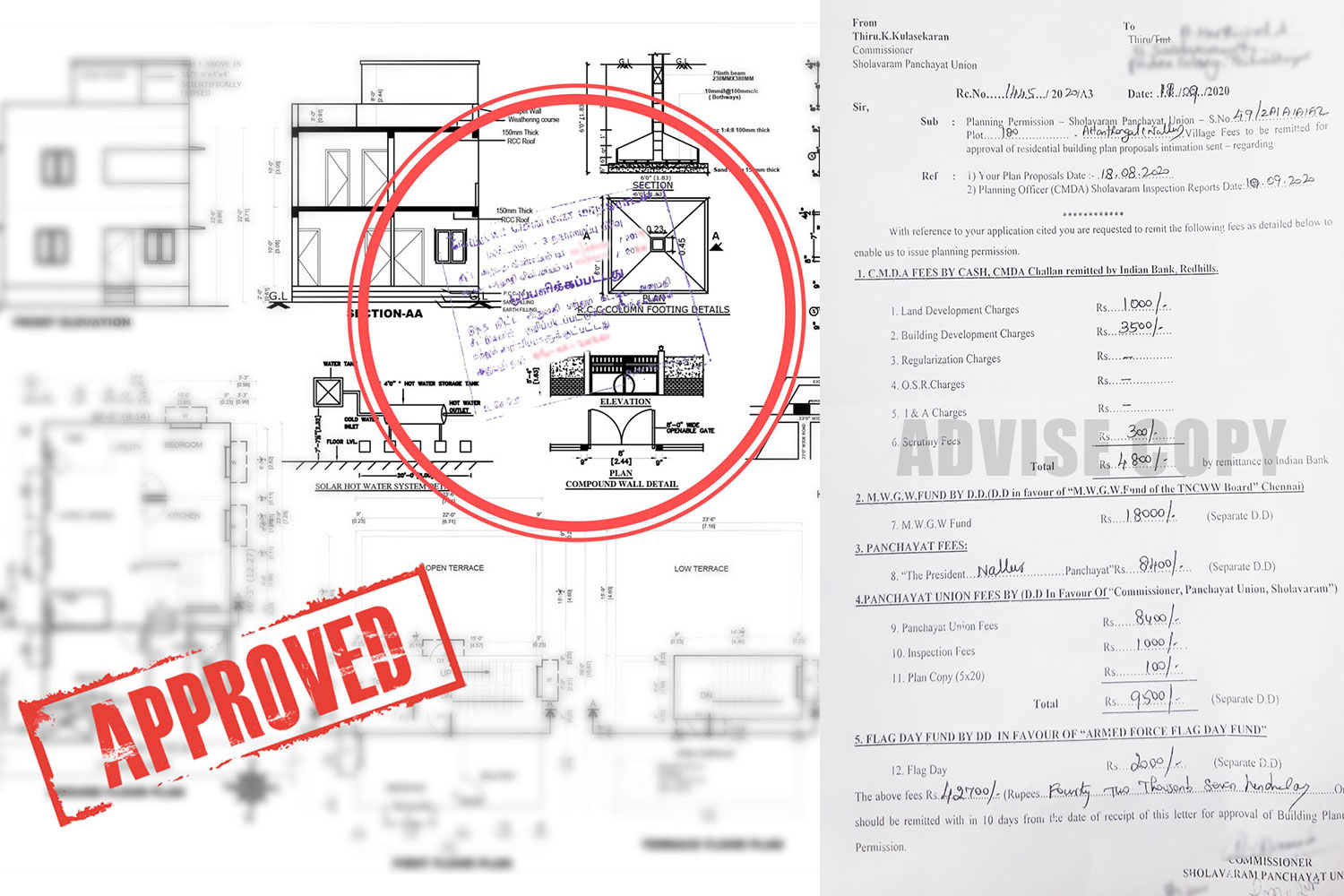
4. Plan Approval
Once the zoning and land use regulations are thoroughly understood, the next step is to obtain building plan approval. The building plan, which includes architectural designs, structural plans, and adherence to building codes, must be submitted to the local municipal corporation or development authority. The approval process involves a detailed review to ensure that the proposed construction complies with safety standards, building codes, and environmental regulations.
Issued by : Municipal Corporation


5. Layout Approval
Layout approval is a crucial step in the construction process, particularly for large-scale residential or commercial projects. It involves obtaining approval for the overall layout plan of the project, including the arrangement of plots, roads, open spaces, and amenities. This ensures that the development adheres to urban planning standards and regulations.
Issued by : DTCP, HMDA



6. RERA Registration
In addition to the above approvals, it is mandatory to register the project with the respective state Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA). RERA registration ensures transparency, protects the interests of homebuyers, and promotes accountability among builders and developers. Obtaining the RERA registration number and complying with its regulations is crucial for all residential projects.
Issued by : RERA



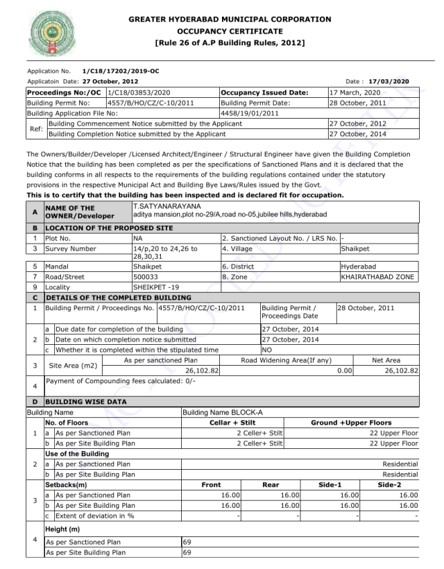
7. Occupancy Certificate
Occupancy Certificate is the final certificate to be received for a project. It implies that the property is now fit for occupation.
Issued by : GHMC, HMDA